
Serial v.s. Parallel [1][2]
Serial communication data is transferred serially (one after another) and not parallel (everything together). So as expected, a serial communication can be done using fewer wires as compared to its parallel counterpart and it also needs some sort of syncing mechanism (clock) to make a successful communication.
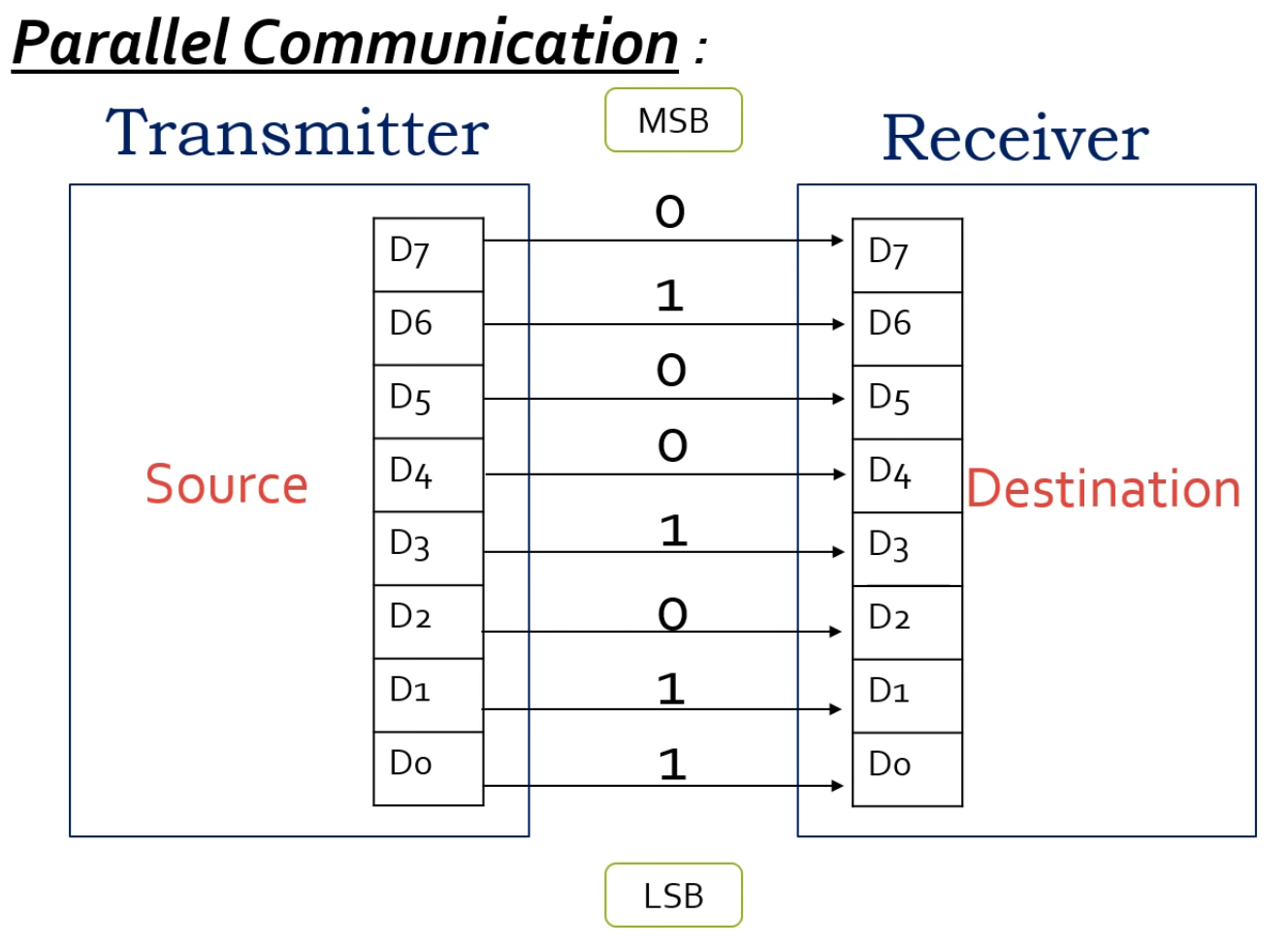
Asynchronous v.s. Synchronous [1][2]
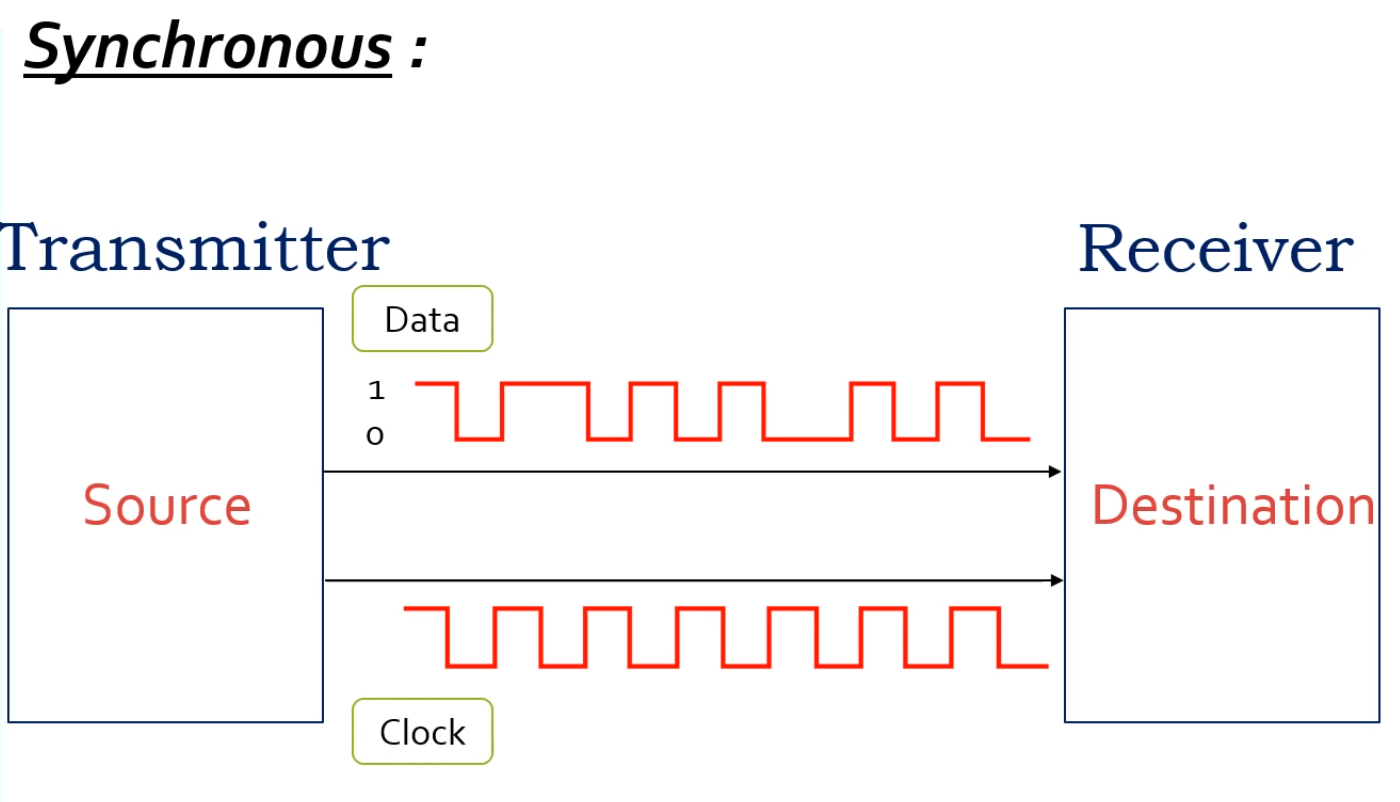
Synchronous serial communication: In this type of communication both transmitter and receiver share a common clock to remain in sync with each other. Asynchronous serial communication: This type of serial communication does not require any common clock source between the transmitter and receiver, both the sides work according to their independent clocks.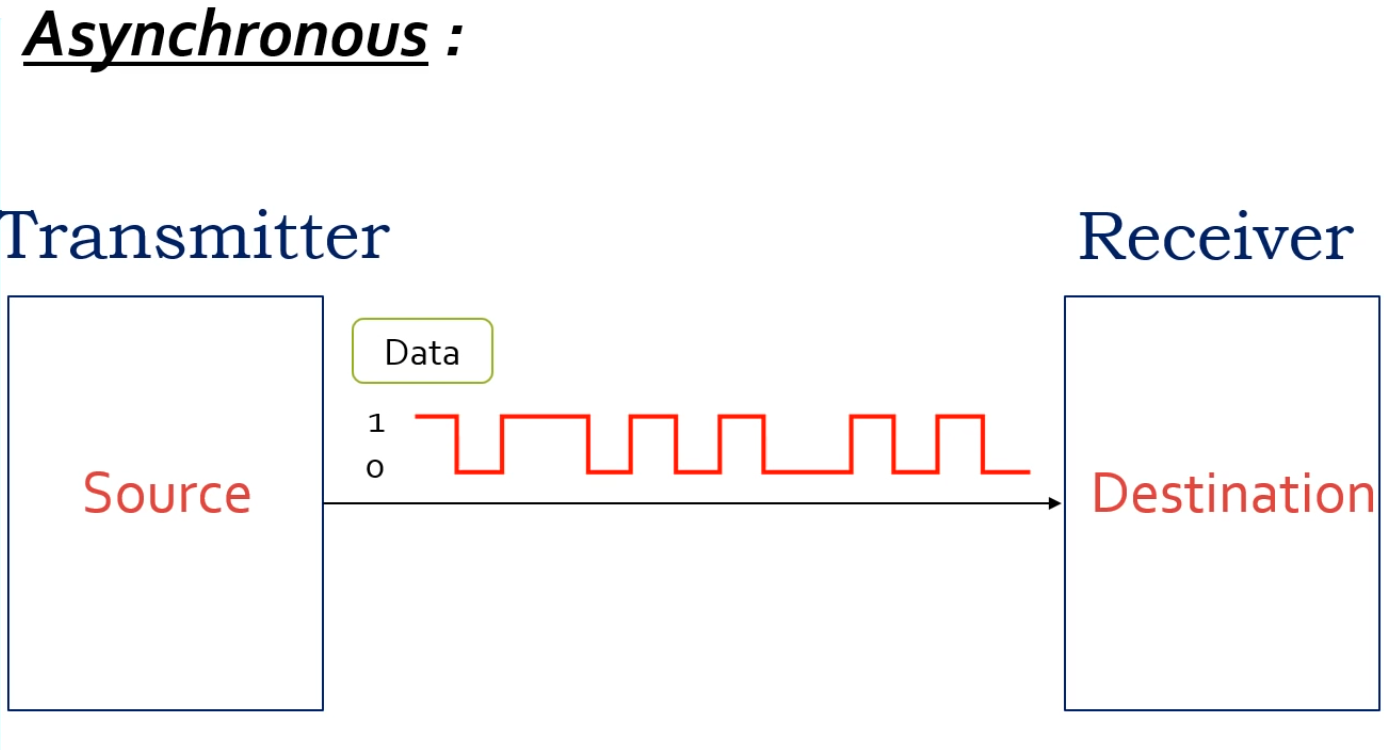
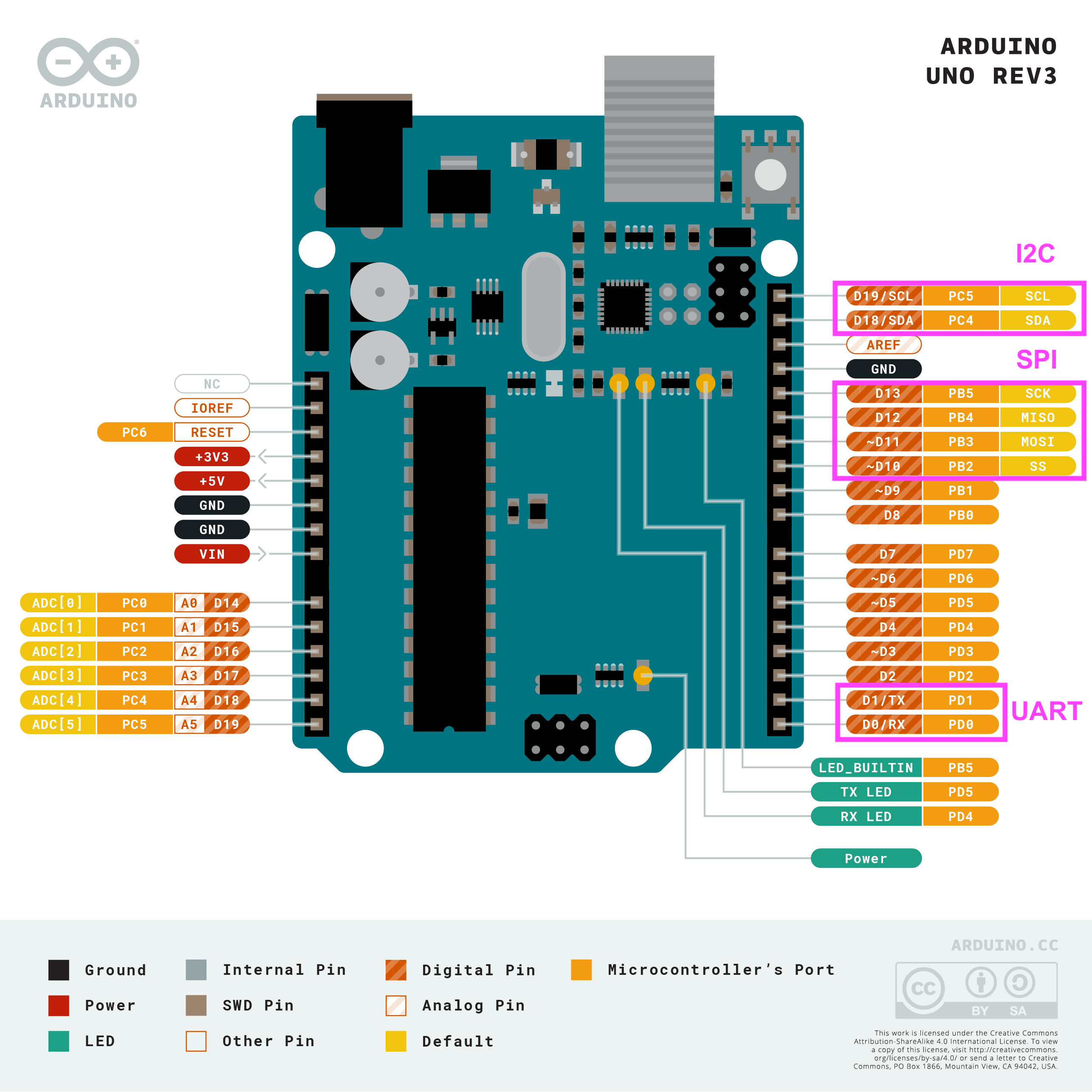
Serial Communication on Arduino Uno
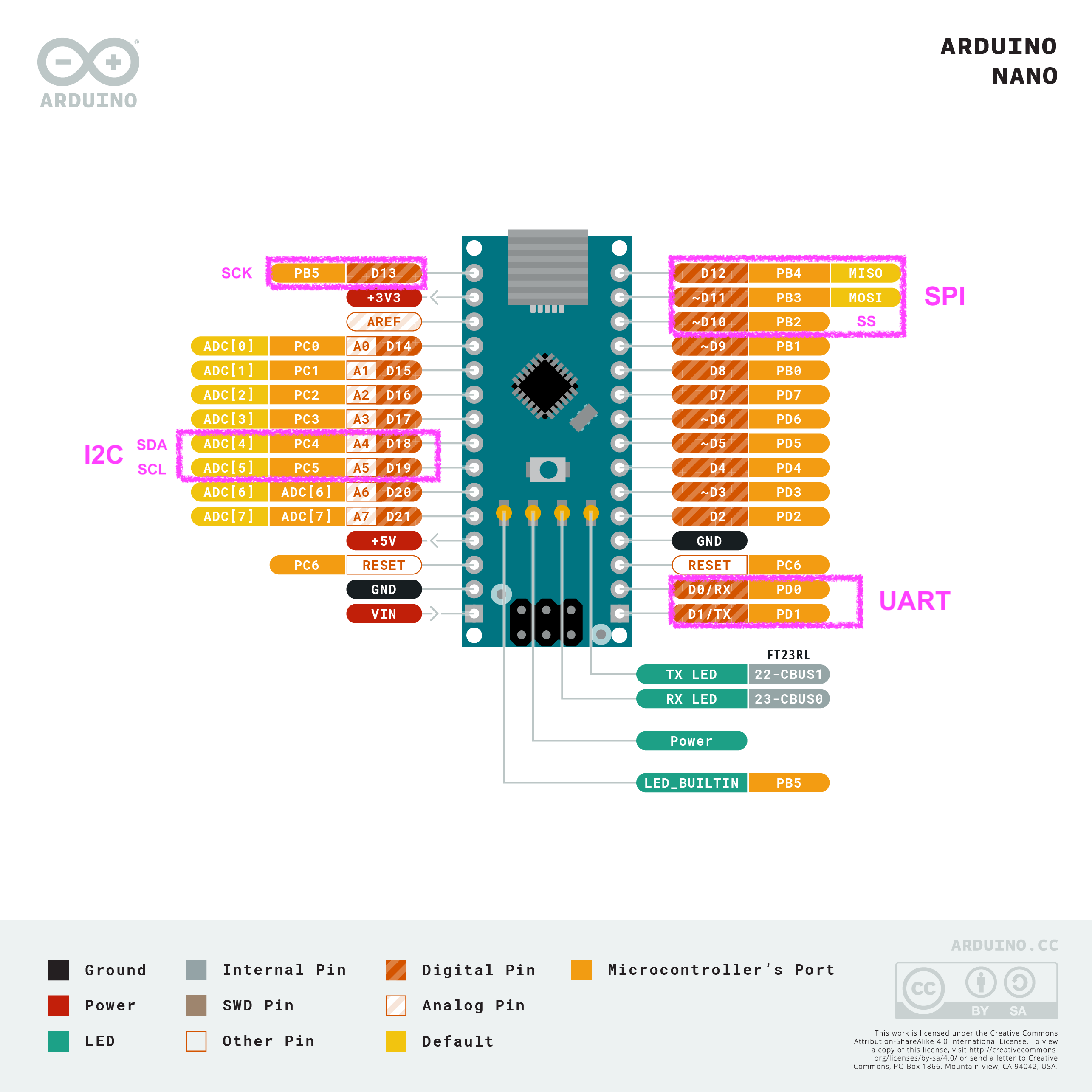
Serial Communication on Arduino Nano
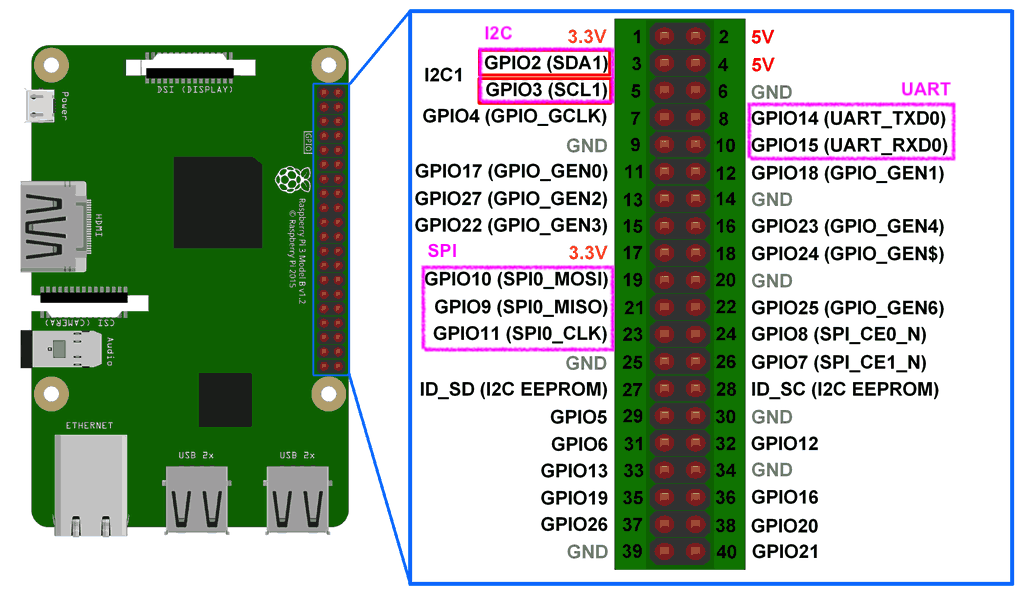
Serial Communication on Raspberry Pi (RPi) [3]
Serial Communication: UART v.s. I2C v.s. SPI
| UART | I2C | SPI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Name | Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter | Inter-Integrated Circuit | Serial Peripheral Interface |
| Connection | |||
| SYN | Asynchronous | Synchronous | Synchronous |
| Wires | 2 (RX, TX) | 2 (SCL, SDA) | 3 (SCLK, MISO, MOSI) + N (SS) |
| Devices | 1 to 1 | N Masters, N Slaves | 1 Master, N Slaves |
| Receiver and Transmitte | Simplex or Half-Duplex or Full-Duplex | Half-Duplex | Full-Duplex |
| Speed | 9.6/19.2/38.4/57.6/115.2 kbps | 100/400 kbps | a few mbps |
| Distance | around 15m | around 1m | around 0.2m |
| Power | medium | medium | lower |
| Error Detection | parity bit | no | no |
| Flow Control (Acknowledgement Mechanism) | no | ACK bit | no |
| Data Start From | LSB First | MSB First | LSB or MSB First |
| Data Transmission | Frame (start bit, data bits, parity bit, stop bit) | Address (start bit, device address 8 bits, ack, internal register address 8 bits, ack, data 8 bits, ack, stop bit) | Slave Select/Chip Select. Active low, it is pulled high to disconnect the slave from the SPI bus. |
Read more details:
SPI: https://shannon112.blogspot.com/2021/01/embedded-system-serial-peripheral.html
I2C: https://shannon112.blogspot.com/2021/01/embedded-system-inter-integrated.html
UART: https://shannon112.blogspot.com/2021/01/embedded-system-universal-asynchronous.html
Reference
[1] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IyGwvGzrqp8
[2] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MebhACqcdno
[3] https://www.engineersgarage.com/raspberrypi/articles-raspberry-pi-i2c-bus-pins-smbus-smbus2-python/
Read in markdown version: https://github.com/shannon112/Notes/blob/main/serial_com_comparison/README.md

0 comments:
張貼留言
留言